Water conservation refers to reducing the use of water.
The goals of water conservation efforts include:
- Sustainability - To ensure availability for future generations, the withdrawal of fresh water from an ecosystem should not exceed its natural replacement rate.
- Energy conservation - Water pumping, delivery, and wastewater treatment facilities consume a significant amount of energy. In some regions of the world (for example, California).
- Habitat conservation - Minimizing human water use helps to preserve fresh water habitats for local wildlife and migrating waterfowl, as well as reducing the need to build new dams and other water diversion infrastructure.

The old way — wasteful homes
Showers, toilets, and gardening — the big uses
- Bathing and cleaning - 28%
- Laundry and dishes - 16%
- Drinking and cooking - 4%
- Garden watering - 20%
- Toilet flushing - 32%







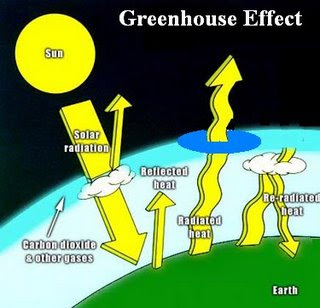
 Ozone Layer: A gaseous layer of the chemical ozone present in the atmosphere protecting the Earth from ultraviolet radiation. Ozone layer helps to produce the observed vertical structure of the atmosphere, and absorbs harmful ultraviolet radiation that would otherwise damage plant and animal life (also causing skin cancer) on the Earth’s surface. Hence Ozone is like an Anti-virus installed in our system which rescues our computer from virus threats.The ozone layer is thinnest near the equator and thickest at the poles. Since ozone formation depends on ultraviolet radiation from the Sun, the amount of ozone present in the atmosphere at any given time and place varies. Also, the lifetime of an ozone molecule in the stratosphere is between several months and several years, so the distribution of ozone is affected by the motion of the atmosphere; ozone molecules can be transported long distances before being destroyed.
Ozone Layer: A gaseous layer of the chemical ozone present in the atmosphere protecting the Earth from ultraviolet radiation. Ozone layer helps to produce the observed vertical structure of the atmosphere, and absorbs harmful ultraviolet radiation that would otherwise damage plant and animal life (also causing skin cancer) on the Earth’s surface. Hence Ozone is like an Anti-virus installed in our system which rescues our computer from virus threats.The ozone layer is thinnest near the equator and thickest at the poles. Since ozone formation depends on ultraviolet radiation from the Sun, the amount of ozone present in the atmosphere at any given time and place varies. Also, the lifetime of an ozone molecule in the stratosphere is between several months and several years, so the distribution of ozone is affected by the motion of the atmosphere; ozone molecules can be transported long distances before being destroyed.
 Ozone is formed in the atmosphere when ultraviolet radiation from the Sun splits one oxygen molecule into two oxygen atoms (O2). The atomic oxygen then combines with another oxygen molecule to form ozone (O3). Most ozone found in the Earth’s atmosphere occurs in one layer in the stratosphere, between altitudes of around 20 to 50 km (12 to 30 mi).
Ozone is formed in the atmosphere when ultraviolet radiation from the Sun splits one oxygen molecule into two oxygen atoms (O2). The atomic oxygen then combines with another oxygen molecule to form ozone (O3). Most ozone found in the Earth’s atmosphere occurs in one layer in the stratosphere, between altitudes of around 20 to 50 km (12 to 30 mi).